Education is the foundation of a brighter future, but access to quality learning resources remains a challenge for many students in low-income communities.
Digital literacy, which is the ability to use technology effectively for learning, has the power to bridge this gap.
Non-profit organizations across Nigeria are stepping up to equip students with digital skills, ensuring they are not left behind in an increasingly digital world.
By integrating technology into education, students gain access to better learning tools, improving their academic performance and prospects.
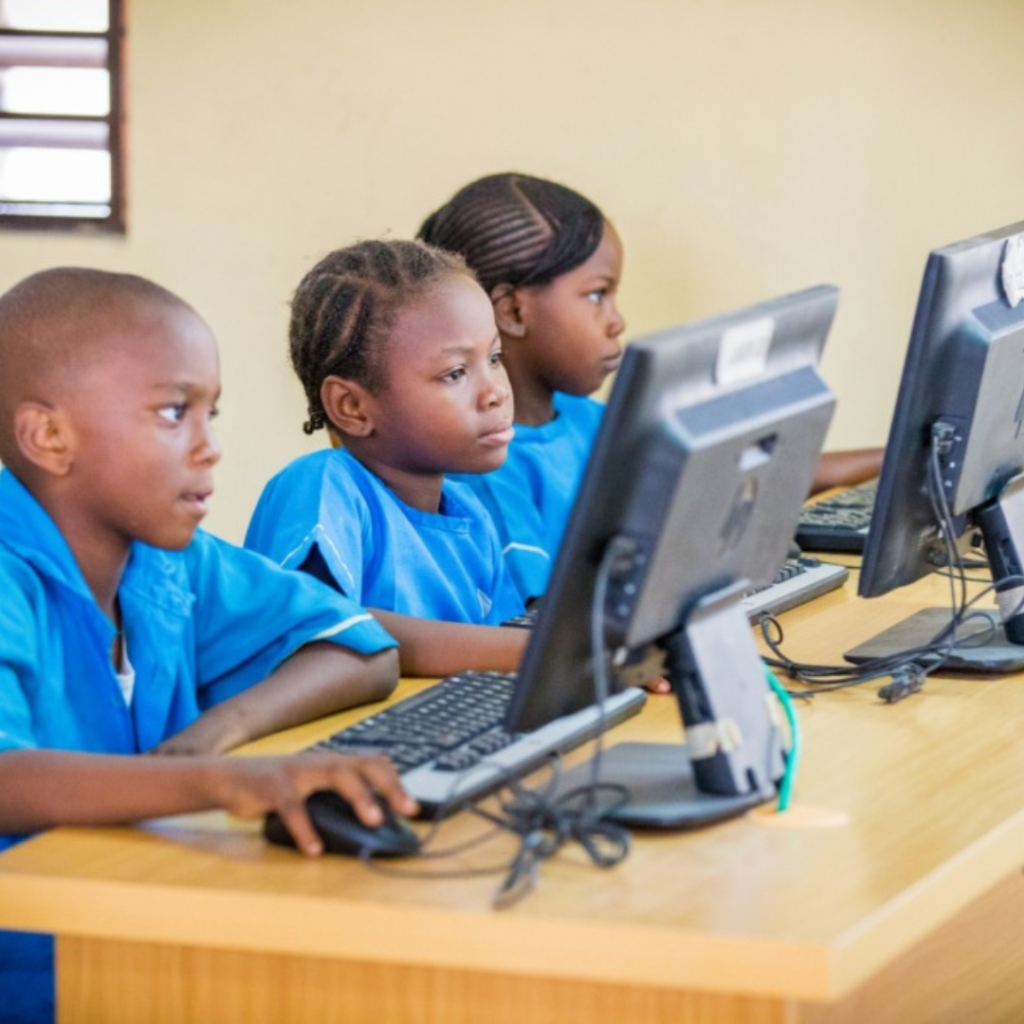

Understanding Digital Literacy in Education
Digital literacy goes beyond knowing how to operate a computer. It includes:
- Accessing Information: Using search engines, digital libraries, and educational websites.
- Communication & Collaboration: Engaging in online discussions, virtual study groups, and e-learning platforms.
- Creativity & Critical Thinking: Learning through interactive tools like coding apps and multimedia content.
Non-profits such as Paradigm Initiative and Teach for Nigeria are introducing digital skills programs to students who lack access to formal digital education. These programs focus on helping students and teachers embrace technology as a learning tool.
The Impact of Digital Literacy on Academic Performance
Integrating digital literacy into education has shown remarkable results:
1. Improved Access to Information
Traditional textbooks are limited, but digital resources provide up-to-date information. Platforms like Khan Academy and Google Scholar allow students to explore a vast range of subjects at their own pace.
2. Enhanced Engagement
Interactive tools, such as educational games and virtual science labs, make learning fun and engaging, helping students retain information better than traditional rote learning methods.
3. Better Retention & Understanding
Video tutorials and infographics simplify complex subjects. For instance, students learning about space can explore virtual solar system models instead of relying on static images in books.
4. Self-Paced Learning
Digital platforms allow students to learn at their own speed. Non-profits like Africa Code Week provide free coding lessons, empowering students to develop skills that enhance their education and career opportunities.
How Digital Literacy Bridges the Education Gap in Nigeria
Supporting Rural & Underserved Schools
Many rural schools in Nigeria lack qualified teachers, but digital literacy programs provide alternative learning methods. One Laptop per Child Nigeria distributes affordable laptops to students in remote areas, giving them access to online courses and resources.
E-learning & Remote Education
During school closures, digital literacy helped students continue learning through online classes. Non-profits like uLesson offer affordable digital tutoring for Nigerian students, ensuring that education is not disrupted.
Addressing Learning Disabilities
Assistive technologies, such as text-to-speech tools and screen readers, help students with disabilities learn effectively. The Special Needs Initiative for Growth provides digital tools to children with disabilities, ensuring inclusive education.

Real-World Success Stories
Case Study 1: Digital Skills Transform a Student’s Future
Amina, a 14-year-old girl from a rural community in Kaduna, struggled with mathematics. Through a non-profit digital literacy program, she gained access to an online tutoring platform. Today, she is excelling in school and dreams of becoming an engineer.
Case Study 2: A School Adopts Digital Learning
A public secondary school in Lagos implemented a non-profit-funded e-learning initiative, improving students’ performance by 30% within a year. Teachers received digital training, enabling them to integrate technology into their lessons effectively.
Case Study 3: From a Rural Village to a Global Stage
A young student in Enugu, with no prior digital experience, joined a non-profit coding bootcamp. Today, he is building mobile apps and has secured an internship with a tech company.
Challenges in Implementing Digital Literacy in Schools
Despite its benefits, digital literacy adoption faces several obstacles:
- Limited Internet & Power Supply: Many rural areas lack stable electricity and internet connectivity.
- High Cost of Digital Devices: Laptops and tablets remain unaffordable for low-income families.
- Teacher Training Gaps: Many educators lack digital skills and require specialized training.
- Resistance to Change: Some parents and administrators are skeptical about digital learning.

Strategies for Expanding Digital Literacy in Nigerian Education
To maximize the impact of digital literacy, non-profits, government agencies, and private sector players must collaborate.
- Government & NGO Support
- Increased investment in digital infrastructure.
- Subsidized internet access for schools.
- Public-Private Partnerships
- Tech companies donating computers and software.
- NGOs offering free training for teachers and students.
- Community Involvement
- Encouraging parents and community leaders to support digital education.
- Creating local learning centers with digital access.
- Affordable Learning Solutions
- Developing offline digital tools for areas with no internet.
- Promoting low-cost mobile learning applications.
Conclusion
Digital literacy is no longer a luxury, it is a necessity for academic success. Through non-profit programs, Nigerian students in low-income areas are gaining the skills they need to compete in a digital world.
By expanding digital access, training teachers, and supporting students, we can create a future where every child, regardless of their background, has an equal opportunity to succeed.
Non-profits, government agencies, and private sector organizations must continue working together to ensure digital literacy is accessible to all.






