In today’s digital age, the gap between urban and rural areas is more apparent than ever. While cities flourish with high-speed internet, advanced technology, and digital skills, many rural communities are left behind.
According to the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), only 28% of rural households worldwide have internet access compared to 79% in urban areas.
This disparity limits opportunities for rural residents to compete and thrive in a modern world.
Digital literacy is a transformative tool to bridge this divide, enabling economic growth, education equity, and social inclusion.
Understanding the Urban-Rural Divide
The urban-rural divide refers to the disparity in access to technology, resources, and opportunities between cities and rural areas. Several factors contribute to this gap:
- Infrastructure Deficits: Many rural areas lack reliable internet connectivity and electricity.
- Economic Constraints: High poverty rates in rural regions limit access to devices and data plans.
- Educational Disparities: A lack of schools equipped with digital tools hinders rural students from gaining essential skills.
- Cultural Barriers: Resistance to new technologies due to traditional practices further widens the divide.
These challenges perpetuate a cycle of inequality, limiting rural communities’ ability to participate in a digitally-driven economy.
Insert Image: A rural classroom with outdated teaching tools versus an urban classroom with advanced digital technology.
What is Digital Literacy?
Digital literacy is more than just using a computer or smartphone. It encompasses the skills required to navigate, evaluate, and create information through digital tools effectively. Key components of digital literacy include:
- Basic Skills: Operating devices, using search engines, and managing emails.
- Advanced Skills: Coding, data analysis, and e-commerce management.
- Digital Safety: Understanding online security, privacy, and responsible digital behavior.
Digital literacy enables individuals to leverage technology for education, work, and personal development, making it a cornerstone for bridging the urban-rural divide.
Benefits of Digital Literacy in Bridging the Divide
1. Economic Empowerment
Digital literacy empowers rural entrepreneurs to tap into global markets through e-commerce platforms. For instance, rural artisans in Kenya sell handmade crafts internationally via platforms like Jumia and Etsy. Moreover, digital skills open doors to remote work opportunities, allowing individuals to earn without relocating to urban centers.
Insert Image: A rural artisan using a smartphone to sell handmade goods online.
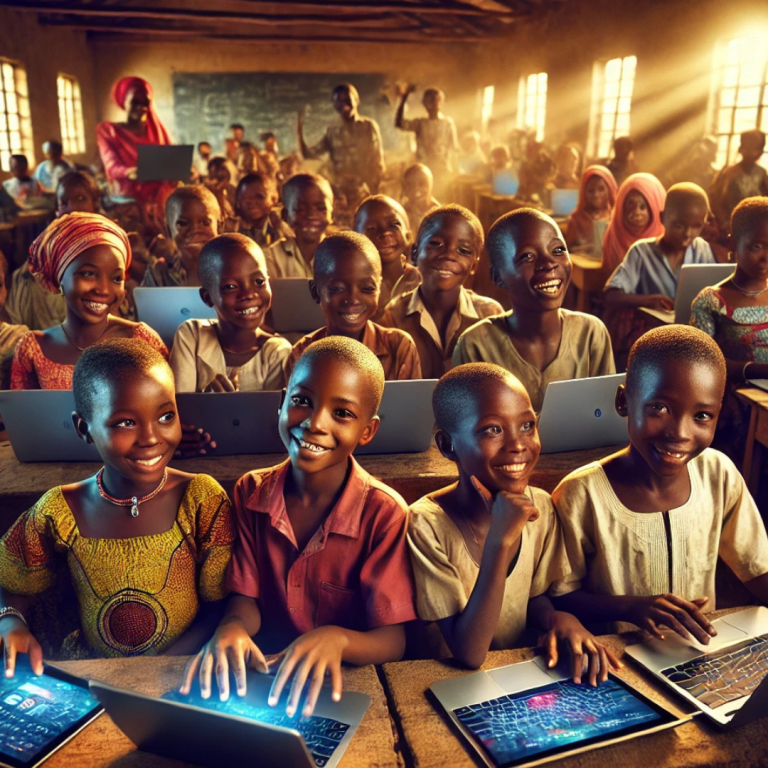
2. Improved Education
Online learning platforms such as Coursera, Udemy, and YouTube bridge the education gap by providing access to quality resources for rural students. Virtual classrooms allow teachers in remote areas to connect with urban experts, enhancing the learning experience.
Insert Image: A group of rural students attending an online class on laptops provided through a community initiative.
3. Better Healthcare Access
Digital literacy also improves healthcare delivery in rural areas. Telemedicine platforms connect patients with doctors, eliminating the need for long-distance travel. Mobile health apps and SMS campaigns provide vital health information, improving awareness and outcomes.
Insert Image: A rural woman consulting a doctor via a telemedicine app on her phone.
4. Social Inclusion
Digital literacy reduces social isolation by enabling rural residents to connect with others via social media and online networks. It also raises awareness about rights, opportunities, and current events, fostering greater integration into society.
Real-Life Success Stories
Case Study 1: Rural Entrepreneurs in Nigeria
Fatima, a farmer in Kaduna, struggled to sell her produce locally. After attending a digital marketing workshop, she started promoting her products on WhatsApp and Facebook, reaching urban buyers and increasing her income.
Case Study 2: Telemedicine in India
A telehealth initiative in Bihar connects rural patients with urban doctors, saving time and reducing healthcare costs. This program has significantly improved maternal health outcomes in the region.
Case Study 3: Digital Literacy Programs in Kenya
An NGO introduced free digital skills training in a remote Kenyan village. Within a year, many participants secured remote jobs or started online businesses, transforming their community’s economic landscape.
Challenges to Promoting Digital Literacy in Rural Areas
Despite its benefits, promoting digital literacy in rural areas faces significant obstacles:
- Infrastructure Gaps: Unreliable electricity and poor internet connectivity hinder access.
- High Costs: Smartphones, laptops, and data plans remain unaffordable for many rural families.
- Cultural Resistance: Traditional norms and skepticism about technology delay adoption.
- Gender Inequality: Women in rural areas often face additional barriers, such as limited access to education and restrictive societal norms.
Insert Image: A rural family using a single shared mobile phone due to affordability issues.
Solutions for Bridging the Urban-Rural Divide Through Digital Literacy
1. Infrastructure Development
Investing in broadband networks and renewable energy sources can improve connectivity in rural areas. Initiatives like Google’s Project Loon and SpaceX’s Starlink are already addressing these gaps.
2. Affordable Technology
Providing subsidized devices and internet plans ensures accessibility for low-income households. Rwanda’s “One Laptop Per Child” program is an excellent example of this approach.
3. Localized Training Programs
Training initiatives tailored to local languages and cultural contexts can accelerate digital adoption. Programs like Nigeria’s Paradigm Initiative teach practical digital skills to underserved communities.
4. Inclusive Policies
Gender-specific programs, such as SheTrades in Africa, empower rural women to access digital tools and opportunities, fostering greater equality.

Broader Impact of Digital Literacy
Bridging the urban-rural digital divide has far-reaching benefits:
- Economic Growth: Inclusion of rural populations boosts national productivity.
- Education Equity: Equal access to learning resources narrows the education gap.
- Reduced Migration: Opportunities in rural areas reduce pressure on urban centers.
- Social Cohesion: A digitally connected society fosters unity and shared progress.
Conclusion
Digital literacy is a powerful tool to bridge the urban-rural divide, creating equitable opportunities for economic, educational, and social advancement. While challenges persist, collaborative efforts from governments, NGOs, and private organizations can pave the way for a digitally inclusive future. By investing in digital literacy, we can ensure that rural communities thrive alongside their urban counterparts, building a world where opportunity knows no boundaries.






